In today’s fast-paced world of e-commerce and supply chain logistics, warehouses are more than just storage spaces; they are active hubs where efficiency, speed, and accuracy are the key success factors. Old warehouse management methods are finding it difficult to keep up with the growing demand for efficiency and same-day delivery.
Today’s customers want more from distributors: more options, better availability, and a nicer service experience. This makes it harder for distributors to run things efficiently given more competition and quickly changing markets. One of the major challenges is to maintain products in inventory accurately and to ensure the items are handled and shipped correctly.
Table of Contents
Shaping Smart Warehouses: Exploring Computer Vision’s Applications
This is where Warehouse Automation comes in; technology performs tasks and processes with little or no human intervention. Robotic deployment, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), conveyor systems as well as software solutions such as warehouse management systems (WMS) are all included.
They focus on making the process more smooth, concise, fast, and accurate. Warehouse automation is greatly influenced by computer vision (CV). Here, it empowers machines to interpret and comprehend visual information using cameras and apply it to automating traditional human tasks.
First, let’s understand what is Computer Vision (CV) in Warehouse Management.
Computer vision is an aspect of artificial intelligence that allows computers and systems to extract useful information from live visual feedback such as images, videos, or cameras. Copying the way a human eye works, computer vision sees and interprets visual data in terms of identifying objects, tracing movements, recognizing patterns, and even making decisions or predictions.
Methods from machine learning, image processing, and deep learning are employed to make machines “see” and act appropriately in different uses. Let’s understand in detail the role and applications of CV in warehouse management in this article.
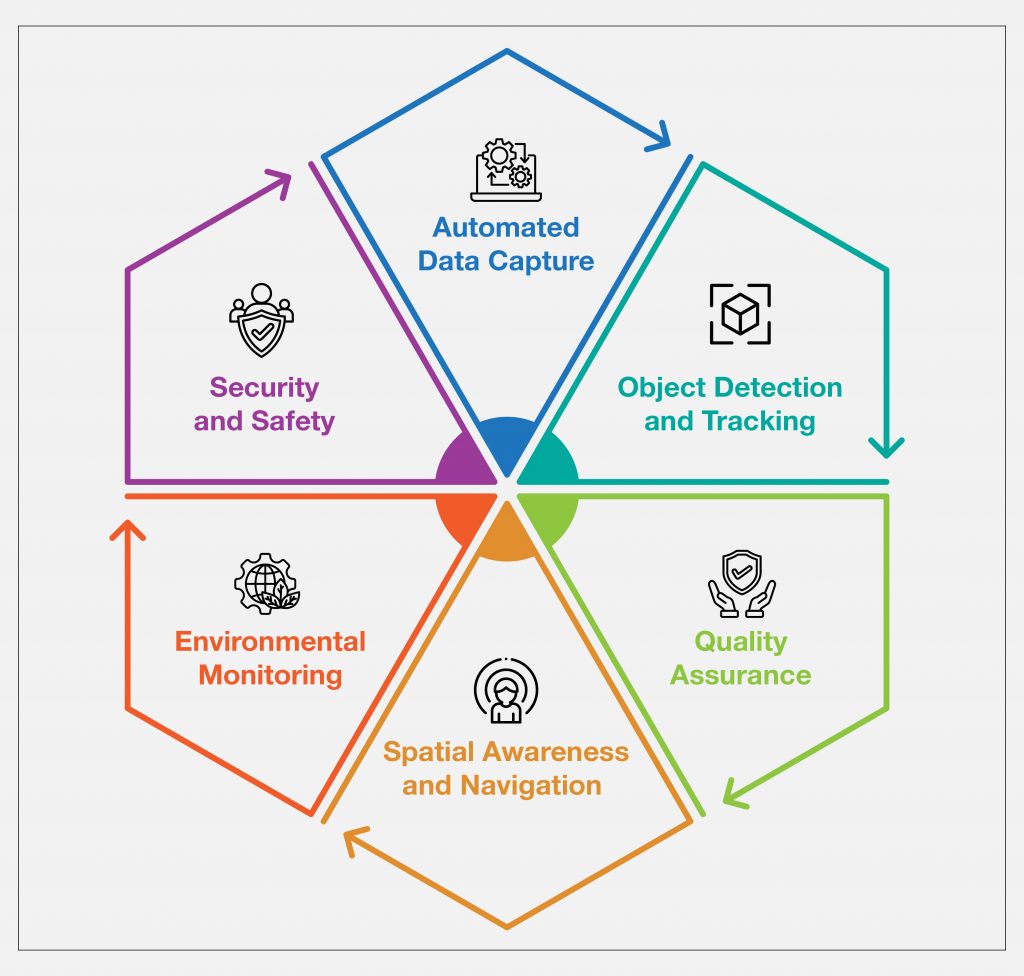
1.Automated Data Capture
Visual data is captured constantly by computer vision systems, converting that data into actionable insights. This reduces manual data entry and checks for real-time updates to run accurate warehouse operations.
2.Object Detection and Tracking
CV algorithms track items, such as products and pallets, as they move. It keeps inventory records and stores optimally as well.
3.Quality Assurance
Computer vision is to recognize defects, damages, or quality problems from visual data. This ensures product standards and reduces the number of shipment errors.
4.Spatial Awareness and Navigation
Robots can learn environments safely and efficiently by understanding them through CV. Accessing obstacles, finding optimal paths, and cooperating with humans without any obstacles.
5.Environmental Monitoring
Temperature, humidity, and other conditions are monitored by vision systems that ensure proper storage. It is necessary to preserve the quality of sensitive or perishable goods.
6.Security & Safety
Computer vision secures unauthorized access and theft by detecting them. This also helps improve workplace safety as it helps identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety protocols.
| [Download Ebook] Enhancing Quality Control in Manufacturing by leveraging Computer Vision |
So, how do we at “Gramener” unlock efficiency in warehouse management? What are the key applications of computer vision in this? Let’s understand various applications.
1.Inventory Tracking
Computer vision monitors stock levels in real time. This ensures accurate inventory records that prevent overstock or shortage.
2.Order Picking Support
Vision-powered systems help workers find items quickly and check if they are correct, reducing mistakes in order fulfillment.
3.Automatic Quality Check
Computer-vision-enabled cameras scan and detect defective parts or packaging errors, ensuring that only defect-free products are shipped.
4.Robotics Implementation
It enables robots to be able to move around the warehouse, lift items, and sort packages swiftly and properly.
5.Space Optimization
This focuses on shelf utilization and layouts of warehouses for maximum storage efficiency and optimizes operations.
6.Safety Monitoring
Hazard detection using spills, blockage, or unsafe conditions by computer vision will make the workplace much safer and reduce accidents.
7.Shipment Verification
The scanning and verification of packages coming and going will automatically provide efficient and correct processing.
8.Performance Analytics
Computer vision provides valuable insights into workflow efficiency and bottlenecks, enabling better decision-making and process improvements.
Solutions by Level of Automation
| Category | Basic Automation | Point Automation Systems | Fully Automated |
| Example Technologies | Warehouse management systems (WMS); conveyors; RF scanners; automated pallet wrappers | Cube storage; drones; pallet automated mobile robots (AMRs); automated guided vehicles (AGVs) | Automated cranes; storage and retrieval systems; pick arms in customized lines |
| Why Do It? | Enable easier handling of products and electronic transaction capture | Improve task productivity and test limited automation solutions | Maximize capacity and throughput; achieve significant savings |
| Use Cases | Large distribution centres (DCs); cross-docks | Grocery DC case picks; adding automation to existing DCs | Dark stores; micro-fulfillment centers |
Transforms Your Business with Advanced Computer Vision Solutions
Our research indicates that the adoption of sophisticated automation technologies remains low in business-critical warehouse and logistics systems.
So, let’s book a meeting as we, ‘Gramener – A Straive Company’ will help you in smart warehouse management by reducing manual processes and associated errors by automating a range of tasks, such as inventory management, sorting, quality control and safety management, and drive warehouse operations quick and reliable results.

